África e suas culturas: A Rich Tapestry of Diversity and Tradition
Africa is a continent rich in diversity, home to a myriad of cultures, languages, and traditions that have evolved over millennia. Each region boasts its unique practices, beliefs, and art forms, creating a vibrant tapestry that captivates the world. Understanding the depth of Africa’s cultures reveals not only its historical significance but also its influence on global heritage.
From music and dance to visual arts, Africa showcases a dynamic range of cultural expressions. These elements are often intertwined with the continent’s social, spiritual, and political narratives. By exploring these different facets, one can appreciate the intricate relationships that define African societies today.
Migration, colonization, and globalization have shaped the cultural landscape, leading to both the preservation of ancient customs and the emergence of new traditions. Engaging with Africa’s cultures offers insights into human resilience and creativity in the face of change.
Historical Overview of African Cultures
Africa has a rich and diverse array of cultures shaped by historical events and interactions. Key periods include pre-colonial civilizations, the impacts of colonialism, and the cultural evolution following independence.
Pre-Colonial Civilizations
Before European colonization, Africa was home to numerous advanced civilizations. The Kingdom of Mali, known for its wealth and scholarly centers like Timbuktu, exemplified the richness of West African cultures.
In East Africa, the Great Zimbabwe emerged as a significant stone city and trading hub. Similarly, the Ashanti Empire in West Africa showcased political sophistication and rich cultural traditions.
These kingdoms contributed to various art forms, languages, and trade networks, linking Africa to Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. The development of trade facilitated the exchange of ideas, religion, and customs that enriched these vibrant societies.
Influence of Colonialism
Colonialism brought significant disruption to African cultural landscapes. European powers established control over vast territories, often disregarding existing kingdoms and social structures.
This period resulted in forced labor, exploitation of resources, and cultural suppression. Indigenous practices were often marginalized, while colonial narratives dominated education and media.
Despite these challenges, African cultures demonstrated resilience by blending traditional practices with new influences. This dynamic led to the creation of hybrid cultures, particularly seen in languages, music, and art.
Post-Independence Cultural Evolution
Post-independence, African nations began to reclaim and revive their cultural identities. Nationalist movements fostered a renewed interest in traditional languages, art, and music.
Countries like Nigeria and South Africa embraced their diverse heritages, promoting indigenous cultures within educational systems.
The contemporary cultural scene has also seen a rise in the global recognition of African arts, from literature to film. This evolution reflects a commitment to preserving heritage while adapting to modern influences and engaging with global platforms.
Geographical Diversity and Cultural Regions
Africa’s diverse geography contributes significantly to its rich cultural tapestry. The continent contains distinct regions, each with unique landscapes and cultural identities shaped by their environments.
North Africa
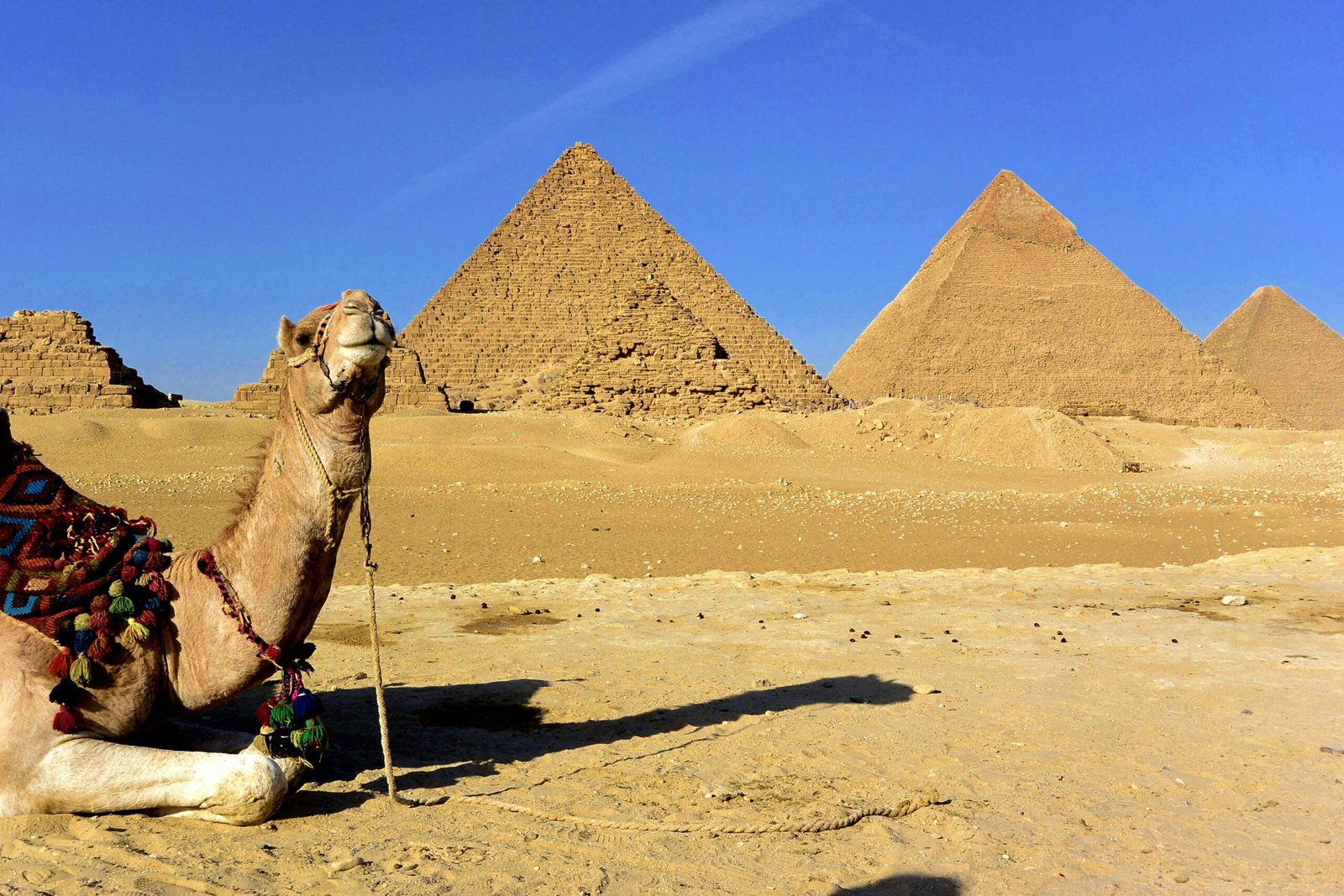
North Africa is characterized by its arid landscapes and Mediterranean coastlines. This region includes countries like Egypt, Libya, Algeria, Tunisia, and Morocco.
The Sahara Desert dominates the landscape, influencing the lifestyles of the Berber and Arab populations. The Nile River is crucial for agriculture and has been vital for Egyptian civilization.
Cultural practices in North Africa reflect a blend of Arab, Berber, and Mediterranean influences. Traditional music, such as Rai, along with rich culinary traditions, showcase the region’s diverse heritage.
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa encompasses a vast area with a variety of climates and ecosystems, ranging from savannas to rainforests. This region includes numerous countries like Nigeria, Kenya, and South Africa.
Cultural diversity is prominent, with thousands of ethnic groups and languages. Each group contributes to a rich array of music, dance, and art forms.
Religious beliefs vary widely, incorporating indigenous, Christian, and Islamic practices. Festivals celebrate agricultural cycles and historical events, fostering community ties.
East and Horn of Africa
East Africa, including countries like Kenya, Ethiopia, and Somalia, is known for its varied geography and cultures. The Great Rift Valley runs through this region, creating unique landscapes and habitats.
Ethiopia stands out for its ancient civilization, historical sites, and its own calendar. The region is also home to diverse ethnic groups, such as the Kikuyu and Oromo.
Cultural practices include coffee ceremonies, unique culinary traditions, and vibrant music styles like Taarab. The cuisine often features injera and spiced dishes, reflecting the local ingredients.
West Africa
West Africa includes nations like Nigeria, Ghana, and Senegal, showcasing a multitude of cultures and languages. The region is rich in cultural heritage, with celebrated traditions in music, art, and oral storytelling.
The Niger River is pivotal for trade and sustenance, shaping the daily lives of many communities.
West African music, such as Afrobeats and Highlife, has gained international recognition. Festivals, often involving traditional dances and costumes, play a significant role in preserving cultural identity.
Central Africa
Central Africa is primarily covered by tropical rainforests, notably the Congo Basin. Countries like the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Cameroon are situated here.
This region is rich in biodiversity, influencing the lifestyle of indigenous groups, such as the Pygmies. Their deep connection to the forest is evident in their traditions and subsistence practices.
Cultural expressions often include intricate wood carvings and masks used in rituals. Music and dance are vital, reflecting communal values and indigenous spirituality.
Southern Africa
Southern Africa is diverse, featuring deserts, savannas, and coastal regions. Countries like South Africa, Namibia, and Botswana showcase varied cultures influenced by indigenous peoples, colonial histories, and contemporary developments.
The region is known for its mineral wealth, affecting economic activities and cultural exchanges.
Cultural traditions include Zulu and Xhosa practices, with music and dance central to community life. Festivals and arts provide a platform for cultural expression, reflecting both historical and modern influences.













Publicar comentário