Renewable Energy: A Sustainable Path Forward
In recent years, the discourse surrounding energy production has undergone a significant transformation. As concerns about climate change, resource depletion, and environmental degradation grow, the focus has shifted increasingly toward renewable energy sources. This post will explore the various types of renewable energy, their benefits, challenges, and the crucial role they play in our sustainable future.
What is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are replenished at a rate faster than they are consumed. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute to environmental degradation, renewable energy sources offer a sustainable alternative. The most common types of renewable energy include:
- Solar Energy
- Wind Energy
- Hydropower
- Biomass
- Geothermal Energy
Solar Energy
Solar energy harnesses sunlight using photovoltaic cells or solar thermal systems. Its benefits include:
- Abundant Resource: The sun provides more energy in one hour than the entire world consumes in a year.
- Low Environmental Impact: Once installed, solar panels produce electricity with minimal environmental impact.
- Energy Independence: Solar energy can reduce reliance on imported fuels.
However, there are challenges associated with solar energy, such as:
- Intermittency: Solar energy production is dependent on sunlight, making it less reliable during cloudy days or nighttime.
- Space Requirements: Large-scale solar farms require significant land area, which can lead to habitat disruption.
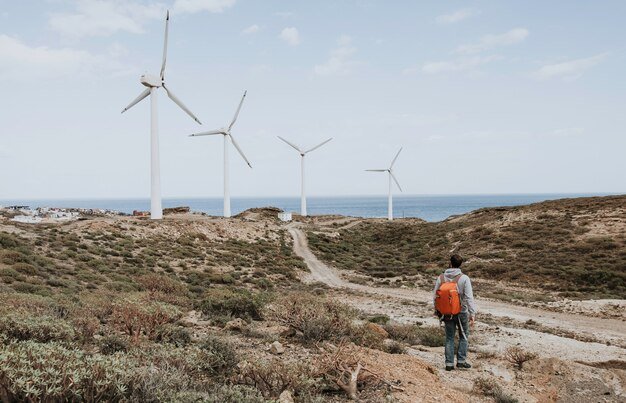
Wind Energy
Wind energy is generated by converting the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical power through turbines. The advantages of wind energy include:
- Clean Energy Source: Wind energy generates electricity without greenhouse gas emissions.
- Job Creation: The wind energy sector has created numerous jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
Challenges for wind energy include:
- Intermittency: Like solar, wind energy production can be unpredictable due to varying wind speeds.
- Aesthetic Concerns: Some communities oppose wind farms due to their visual impact on landscapes.
Hydropower
Hydropower, or hydroelectric energy, is generated by harnessing the energy of flowing water. It has several benefits:
- Reliable and Consistent: Hydropower can produce a constant supply of energy and can be adjusted to meet demand.
- Flood Control and Water Supply: Hydropower plants can help manage water resources, providing additional benefits beyond energy production.
However, hydropower also faces challenges:
- Environmental Impact: Dam construction can disrupt local ecosystems and displace communities.
- Drought Vulnerability: Changes in precipitation patterns can affect water availability for hydropower generation.
Biomass
Biomass energy comes from organic materials, such as plant and animal waste. Its advantages include:
- Waste Reduction: Biomass energy can help reduce waste by repurposing organic materials.
- Carbon Neutrality: Biomass can be considered carbon-neutral, as the CO2 released during combustion is offset by the CO2 absorbed during the growth of the biomass.
However, challenges include:
- Land Use: Cultivating biomass can compete with food production and natural habitats.
- Emissions: While biomass is often considered cleaner than fossil fuels, it can still produce greenhouse gases when burned.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy utilizes heat from the Earth’s interior to generate electricity or provide direct heating. Its benefits include:
- Consistent Energy Production: Unlike solar and wind, geothermal energy can produce a steady supply of energy regardless of weather conditions.
- Small Land Footprint: Geothermal plants require less land compared to other renewable energy sources.
Challenges for geothermal energy involve:
- Geographic Limitations: Not all regions have suitable geothermal resources.
- Initial Costs: The upfront investment for geothermal systems can be high.
The Benefits of Renewable Energy
The transition to renewable energy has far-reaching benefits:
Environmental Impact
Renewable energy sources significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, helping to combat climate change. They also minimize air and water pollution, leading to healthier ecosystems.
Economic Growth
Investing in renewable energy creates jobs and stimulates economic growth. The renewable energy sector has outpaced fossil fuel jobs in recent years, driving innovation and attracting investment.
Energy Security
Diverse energy sources enhance energy security by reducing dependence on imported fuels. By harnessing local renewable resources, countries can stabilize their energy supply.
Social Benefits
Access to clean energy can improve living standards, especially in developing regions. Renewable energy projects can provide electricity to remote areas, enhancing education and healthcare access.
Challenges to Overcome
Despite the benefits, several challenges must be addressed to accelerate the transition to renewable energy:
Infrastructure Investment
Significant investments are needed to upgrade and expand existing energy infrastructure. Smart grids, energy storage systems, and transmission lines must be developed to accommodate renewable sources.
Policy and Regulation
Effective policies and regulations are essential to support renewable energy adoption. Governments must create favorable conditions for investment, including subsidies, tax incentives, and renewable energy targets.
Public Awareness and Acceptance
Public awareness campaigns can help educate communities about the benefits of renewable energy. Engaging local populations in planning and decision-making processes can foster acceptance and support.
Technological Advancement
Ongoing research and development are vital for improving the efficiency and affordability of renewable technologies. Innovations in energy storage, grid management, and energy efficiency will be crucial for maximizing the potential of renewable energy.
The Future of Renewable Energy
The future of renewable energy looks promising. As technology advances and costs continue to decline, the global energy landscape is shifting. Here are some trends to watch:
Increasing Efficiency
Advancements in solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage will continue to improve the efficiency of renewable energy systems, making them more competitive with traditional energy sources.
Integration with Smart Technologies
The integration of renewable energy with smart technologies, such as energy management systems and IoT devices, will enhance grid reliability and optimize energy consumption.
Decentralized Energy Systems
Decentralized energy systems, such as microgrids and community solar projects, empower local communities to generate and manage their own energy, increasing resilience and sustainability.
Global Collaboration
International cooperation will be crucial in sharing knowledge, technologies, and best practices for renewable energy development. Global initiatives, such as the Paris Agreement, aim to foster collaboration in combating climate change.
Conclusion
Renewable energy represents a sustainable and viable path forward in addressing the pressing challenges of our time. By harnessing the power of the sun, wind, water, biomass, and geothermal resources, we can create a cleaner, more equitable, and resilient energy future. While challenges remain, the collective effort of governments, businesses, and individuals can drive the transition to a renewable energy economy. Embracing this change is not just an option—it is an imperative for the health of our planet and future generations.












Publicar comentário